FAQ
Frequently Asked Questions
Birds bring color and life to nearly every corner of the planet. With over 10,000 species, they range from the smallest hummingbird to the majestic eagle, each with distinct calls, colors, and behaviors.
Some of the world’s most endangered animals include the Sumatran orangutan, Javan rhino, Amur leopard, and Vaquita porpoise. Conservation efforts are working to protect these species, but many are still critically endangered due to habitat loss, poaching, and climate change.
Animals communicate in many ways, including vocal sounds, body language, scent markings, and even colors. For instance, wolves use howling to locate their pack, while bees perform a "waggle dance" to signal where food is located. Each species has its own unique methods of communication.
Hibernation allows animals to survive winter months when food is scarce. During hibernation, animals slow down their metabolism, conserve energy, and rely on stored body fat to survive. Examples of hibernating animals include bears, bats, and some species of frogs and snakes.
Camouflage helps animals blend into their surroundings, making it harder for predators to spot them or easier for them to sneak up on prey. Animals like chameleons and leaf insects have colors and patterns that allow them to match their environments, providing an evolutionary advantage.
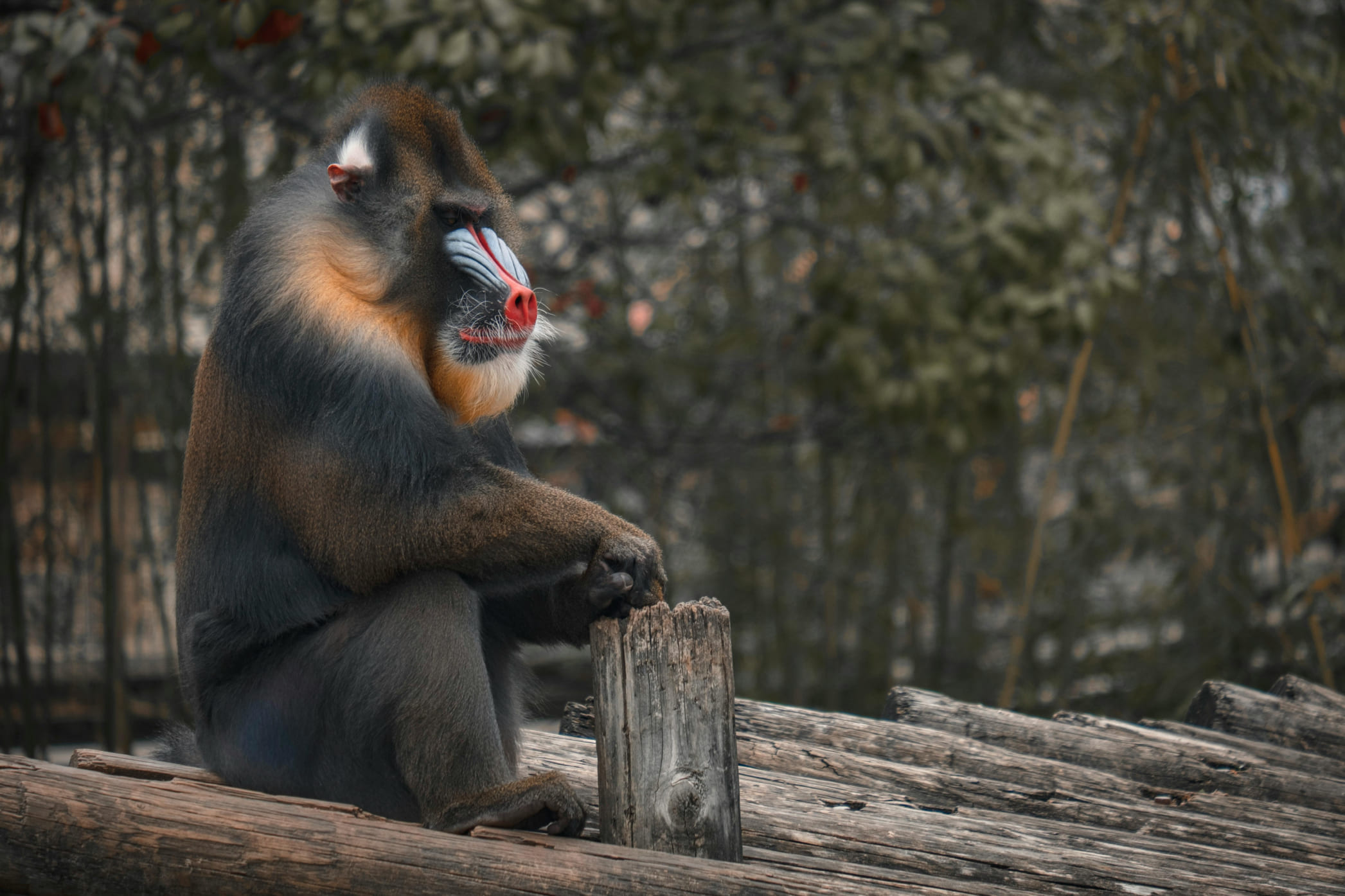

Oceans Alive with Life!
"Oceans cover over 70% of Earth’s surface and teem with life, from coral reefs to deep-sea trenches. Marine life includes species like dolphins, sharks, and plankton, each integral to maintaining the ocean’s ecosystem."
BENEFITS
Benefits & What we do?
Animals adapt in fascinating ways to survive extreme climates. Desert animals like camels store water and have adapted to withstand high temperatures. Polar animals like penguins and polar bears have thick layers of blubber and dense fur to stay warm in icy conditions.
Living in groups offers protection, helps with hunting, and provides social bonding. For example, wolves hunt in packs to take down larger prey, while elephants travel in herds to protect the young. Social structures also help animals communicate and care for each other.
igratory animals use a variety of navigation methods, including the Earth’s magnetic field, the sun and stars, and even scent trails. Birds like the Arctic tern travel thousands of miles each year, often returning to the exact same locations for breeding or feeding.
There are many ways to help protect wildlife! You can support conservation organizations, reduce plastic waste, participate in eco-friendly tourism, and spread awareness about endangered species. Every small action counts towards creating a safer environment for animals.